Describe concepts of relational data
27 Sep 2021
Databases in early days
Problems:
- Every application stored data in its own unique structure.
- When developers wanted to build applications to use that data, they had to know a lot about the particular data structure to find the data they needed.
- Data structures were inefficient, hard to maintain, and hard to optimize for delivering good application performance.
- The relational database model was designed to solve the problem of multiple arbitrary data structures.
- The relational model provided a standard way of representing and querying data that could be used by any application.
Strengths:
- Its use of tables: efficient, and flexible way to store and access structured information.
- Relational databases are used to track inventories, process ecommerce transactions, manage huge amounts of mission-critical customer information, and much more.
- A relational database is useful for storing any information containing related data elements that must be organized in a rules-based, consistent way.
Explore the characteristics of relational data
- One of the main benefits of computer databases is that they make it easy to store information so it’s quick and easy to find.
- An ecommerce system might use a database to record information about the products an organization sells, and the details of customers and the orders they’ve placed.
- A relational database provides a model for storing the data, and a query capability that enables you to retrieve data quickly.
Understand the characteristics of relational data
- Tables -> you model collections of entities from the real world.
- An entity is described as a thing about which information needs to be known or held.
- In the ecommerce example, you might create tables for customers, products, and orders.
- A table contains rows, and each row represents a single instance of an entity.
- The rows in a table have one or more columns that define the properties of the entity, such as the customer name, or product ID.
- All rows in the same table have the same columns. Some columns are used to maintain relationships between tables.
- A relational database by creating a data model.
- The primary key(PK) indicates the column (or combination of columns) that uniquely identify each row. Every table should have a primary key.
- The relationships between the tables.
- 1-to-many(1 customer -> many orders).
- many-to-1(many customers-> many orders).
- A foreign key(FK) also helps to identify and prevent anomalies, such as orders for customers that don’t exist in the Customers table.
- The main characteristics of a relational database :
- All data is tabular.
- All rows in the same table have the same set of columns.
- A table can contain any number of rows.
- A primary key(PK) uniquely identifies each row in a table. No two rows can share the same primary key.
- A foreign key references rows in another, related table.
- Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Use SQL to create tables, insert, update, and delete rows in tables, and to query data.
- Combine the data from multiple tables in a query using a join operation.
- A join operation spans the relationships between tables, enabling you to retrieve the data from more than one table at a time.
Explore relational database use cases
- Use a relational database any time you can easily model your data as a collection of tables with a fixed set of columns.
- If you have a collection of music, video, or other media files, relational database cannot be used but use Azure Blob Storage.
- Social networking sites use databases to store data about millions of users, each of whom can be linked to any number of other users in a highly complex web of relationships. This type of data lends itself more to a graph database structure rather than a collection of relational tables.
- OLTP applications are focused on transaction-oriented tasks that process a very large number of transactions per minute. Relational databases are well suited for OLTP applications because they naturally support insert, update, and delete operations.
- Examples of OLTP applications that use relational databases are:
- Banking solutions
- Online retail applications
- Flight reservation systems
- Many online purchasing applications.
Explore relational data structures
- Index -> An index helps you search for data in a table.
- When the user runs a query that specifies this column in the WHERE clause, the database management system can use this index to fetch the data more quickly than if it had to scan through the entire table row by row.
- An index might consume additional storage space, and each time you insert, update, or delete data in a table, the indexes for that table must be maintained.
- This additional work can slow down insert, update, and delete operations, and incur additional processing charges.
- When deciding which indexes to create, you must strike a balance between having indexes that speed up your queries versus the cost of performing other operations.
- In a table that is read only, or that contains data that is modified infrequently, more indexes will improve query performance.
- If a table is queried infrequently, but subject to a large number of inserts, updates, and deletes (such as a table involved in OLTP), then creating indexes on that table can slow your system down.
- A clustered index physically reorganizes a table by the index key.
- View -> A view is a virtual table based on the result set of a query.
- A view as a window on specified rows in an underlying table.
- Query the view and filter the data in much the same way as a table.
- A view can also join tables together.
On-Primise Databases
- Maintaining the hardware and software, applying patches, backing up databases, restoring them is organization responsibility.
- Scalability is also a concern.
- Data can go offline because of formidable task.
Cloud
- Many of these operations can be handled for you by the data center staff, in many cases with no (or minimal) downtime.
- Free to focus on the data itself and the management concerns to taken care by others (Azure fees).
- No capital expenses, data can be backed up regularly, and companies only have to pay for the resources they use.
- Those organizations plan aggressive expansion on a global basis -> to connect with customers, partners, and other businesses anywhere with minimal effort.
- Instant provisioning because everything is already configured -> eliminated and users can access the application.
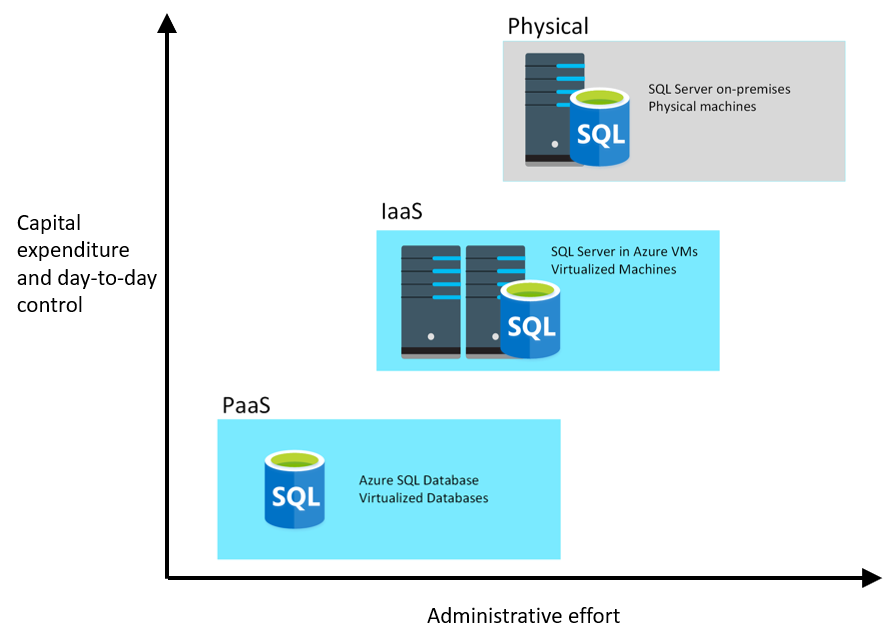
Understand IaaS and PaaS
Infrastructure-as-a-Service(IaaS)
- Create a virtual infrastructure in the cloud that mirrors the way an on-premises data center might work
- Create a set of virtual machines, connect them together using a virtual network, and add a range of virtual devices.
- Companys are responsible for many of the day-to-day operations, such as installing and configuring the software, patching, taking backups, and restoring data when needed.
- The IaaS approach is best for migrations and applications requiring operating system-level access. SQL virtual machines are lift-and-shift (copy your on-premises solution directly to a virtual machine in the cloud).
- Rather than creating a virtual infrastructure, and installing and managing the database software yourself, a PaaS solution does this for you.
- Azure automatically creates the necessary virtual machines, networks, and other devices for you.
- PaaS solutions for relational databases, include Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Azure Database for MySQL, and Azure Database for MariaDB.
- Connect to them, create your databases, and upload your data.
<- Back to Main Menu
