Azure Relational Data Services
28 Sep 2021Introduction
- Database -> Collection of Data
- Shredsheet -> PB of data -> store data in a tabular format, with rows and columns.
- Relationships between tables -> Relational Databases
- Semi-structured or unstructured, comprising of semi-processed or unprocessed data ->non-relational databases.
- DBMS -> physical aspects of a database, such as where and how it’s stored, who can access it, and how to ensure that it’s available when required.
- A stored procedure is a block of code that runs inside your database. Applications often use stored procedures because they are optimized to run in the database environment, and can access data very quickly.
- A linked server is a connection from one database server to another.
- SQL Server can use linked servers to run queries on one server that can include data retrieved from other servers; these are known as distributed queries
Relational Azure Data Services
- Migrate your on-premises systems to a collection of Azure virtual machines.
IaaS(Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
- Create a virtual infrastructure in the cloud that mirrors the way an on-premises data center might work.
- Create a set of virtual machines, connect them together using a virtual network, and add a range of virtual devices. You take responsibility for installing and configuring the software, such as the DBMS, on these virtual machines.
- An Azure Virtual Network is a representation of your own network in the cloud.
- A virtual network enables you to connect virtual machines and Azure services together, in much the same way that you might use a physical network on-premises. Azure ensures that each virtual network is isolated from other virtual networks created by other users, and from the Internet. Azure enables you to specify which machines (real and virtual), and services, are allowed to access resources on the virtual network, and which ports they can use.
PaaS(Platform-as-a-service)
- Creating a virtual infrastructure, and installing and managing the database software yourself, a PaaS solution does this for you.
- Azure automatically creates the necessary virtual machines, networks, and other devices for you
- Scale up or down (increase or decrease the size and number of resources) quickly.
SaaS(Software-as-a-Service)
- Specific software packages that are installed and run on virtual hardware in the cloud.
- Hosted Applications -> Microsoft 365
Azure Data Services
- PaaS category
- Configuration, day-to-day management, software updates, and security of the databases that it hosts.
- Azure SQL Database -> Azure Database for MySQL servers, Azure Database for MariaDB servers, and Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers.
- Available for at least 99.99% of the time.
- Cost -> 1. Base price of each service covers underlying infrastructure and licensing, together with the administration charges.
2. Additionally, these services are designed to be always on. This means that you can’t shut down a database and restart it later.

#### SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines
- IaaS
- Use full versions of SQL Server in the Cloud without having to manage any on-premises hardware.
- SQL Server running on an Azure virtual machine effectively replicates the database running on real on-premises hardware.
- Migrating from the system running on-premises to an Azure virtual machine is no different than moving the databases from one on-premises server to another.
- The database runs stored procedures and scripts as part of the database workload.
- Stored procedures and scripts depend on features that are restricted by following a PaaS approach, then running SQL Server on your own virtual machines might be a good option.
- migrations and applications requiring access to operating system features that might be unsupported at the PaaS level.
- SQL virtual machines are lift-and-shift ready for existing applications that require fast migration to the cloud with minimal changes.
- lift-and-shift refers to the way in which you can move a database directly from an on-premises server to an Azure virtual machine without requiring that you make any changes to it. Applications that previously connected to the on-premises database can be quickly reconfigured to connect to the database running on the virtual machine, but should otherwise remain unchanged.
- A hybrid deployment is a system where part of the operation runs on-premises, and part in the cloud. Your database might be part of a larger system that runs on-premises, although the database elements might be hosted in the cloud.
- #### Azure SQL Database
- PaaS
- SQL Server on a virtual machine ->Management overhead(Disadvantage)
- A SQL Database server is a logical construct that acts as a central administrative point for multiple single or pooled databases, logins, firewall rules, auditing rules, threat detection policies, and failover groups.
- Azure SQL Database options -> Single Database, Elastic Pool, and Managed Instance
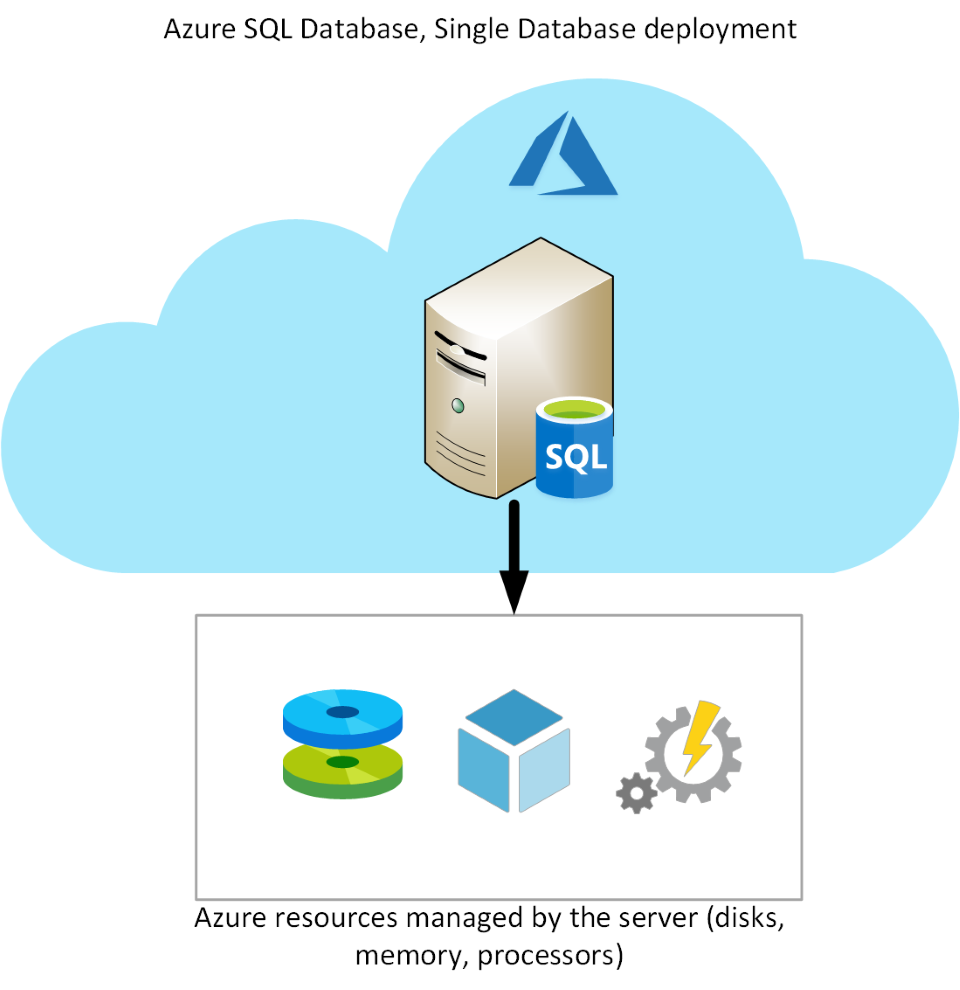
##### Single Database : set up and run a single SQL Server database
- You create and run a database server in the cloud
- You access your database through this server.
- Microsoft manages the server( one should configure the database, create your tables, and populate them with your data.)
- By default, resources are pre-allocated, and you’re charged per hour for the resources you’ve requested.
- A serverless configuration -> Microsoft creates its own server, which might be shared by a number of databases belonging to other Azure subscribers. Microsoft ensures the privacy of your database. Your database automatically scales and resources are allocated or deallocated as required.
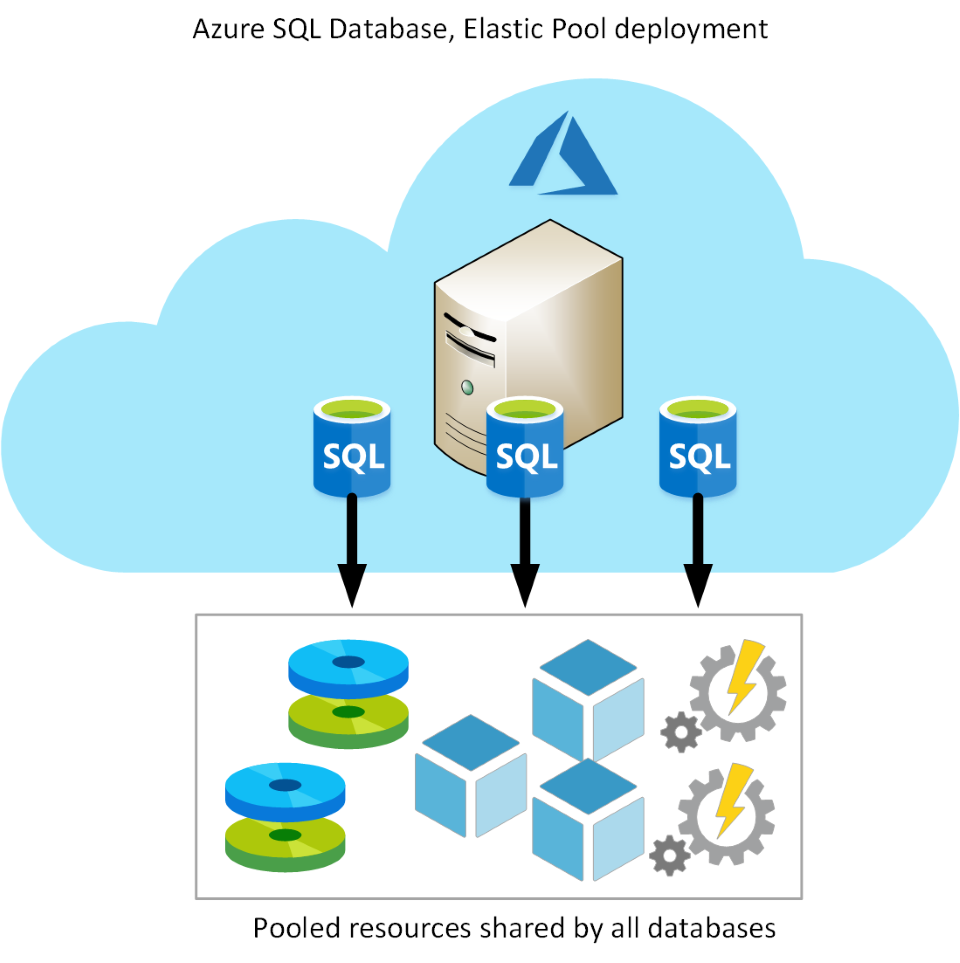
Elastic Pool
- Similar to Single Database, except that by default multiple databases can share the same resources, such as memory, data storage space, and processing power through multiple-tenancy.
- resources ->pool
- create the pool, and only your databases can use the pool
- databases with resource requirements that vary over time, and can help you to reduce costs.
- Elastic Pool enables you to use the resources available in the pool, and then release the resources once processing has completed.
Advantages:
-
Azure SQL Database is often used for:
* Modern cloud applications that need to use the latest stable SQL Server features. * Applications that require high availability. * Systems with a variable load, that need the database server to scale up and down quickly - Advanced threat protection
- At least 99.99% of the time
- Auditing tracks database events and writes them to an audit log
- Secure your data by providing encryption.
- Linked servers are used to perform distributed queries(Single or Elastic pool).
Azure SQL Database Managed Instance
- The Single Database and Elastic Pool options restrict some of the administrative features available to SQL Server.
- Managed instance effectively runs a fully controllable instance of SQL Server in the cloud.
- Automates backups, software patching, database monitoring, and other general tasks, but you have full control over security and resource allocation for your databases.
- All communications are encrypted and signed using certificates. To check the trustworthiness of communicating parties, managed instances constantly verify these certificates through certificate revocation lists.
- If the certificates are revoked, the managed instance closes the connections to protect the data.

PostgreSQL, MariaDB, and MySQL
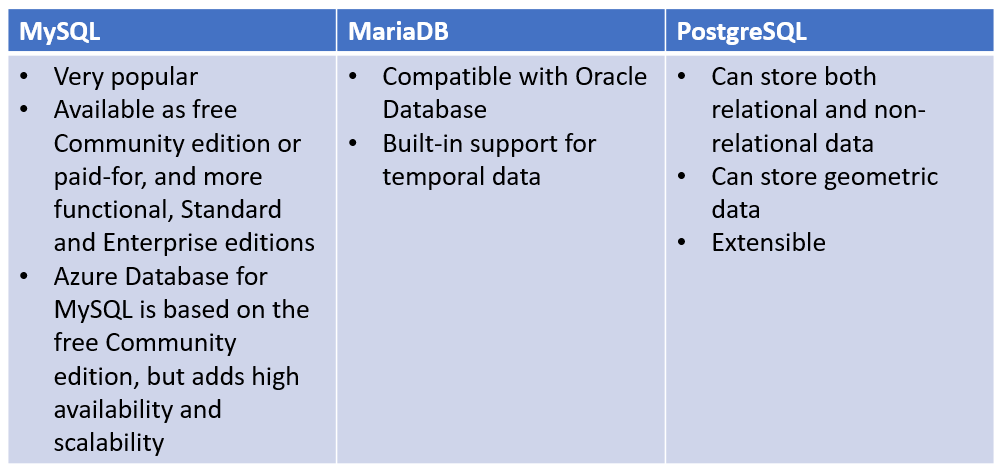
| MySQL | MariaDB | PostgreSQL |
|---|---|---|
| High availability | similar benefits as Azure Database for MySQL | |
| Predictable performance. | Predictable performance | three pricing tiers: Basic, General Purpose, and Memory Optimized |
| Easy scaling | Easy scaling | Hyperscale (Citus) is a deployment option that scales queries across multiple server nodes to support large database loads. Your database is split across nodes. Data is split into chunks based on the value of a partition key or sharding key. |
| Secure data, both at rest and in motion. | Secure data, both at rest and in motion. | highly available service |
| Automatic backups and point-in-time restore for the last 35 days. | pgAdmin tool | |
| Enterprise-level security and compliance with legislation | queries run against databases on the server, and saves them in a database named azure_sys. | |
| ----- | monitor the queries that users are running |
Migrate data to Azure
- Azure Database Migration Service (DMS) -> MySQL, MariaDB, or PostgreSQL databases running on premises on Cloud.
- Restore a backup of your on-premises databases directly to databases running in Azure Data Services.
- Configure replication from an on-premises database, so that any changes made to data in that database are copied to the database running in Azure Data Services.
- Reconfigure users and applications to connect to the database in the cloud.
- don’t have to shut down the on-premises system while you transfer users to the cloud